Smart Pharmaceutical Warehousing
Group Members :
K.R. De Silva E/16/068 (e16069@eng.pdn.ac.lk)
J.M.Praveen Dhananjaya E/16/081 (e16081@eng.pdn.ac.lk)
F.S Marzook E/16/232 (e16232@eng.pdn.ac.lk)
Supervisors
Dr. Isuru Nawinne
Dr. Ziyan Maraikar
Table Of Content
- Problem Overview
- Our solution
- Solution Architecture
- Hardware & Software Designs
- Demonstration and Testing
- Detailed budget
- Final Demonstration
- Documentation
- Related Links
Problem Overview
Conventional pharmaceutical warehouses mostly use manpower to manage and handle goods inside their warehouse complexes. Some warahouses use small indoor vehicles. But all these conventional methods has some inevitable downsides. Most common suhc disadvantages are redundant activities, higher labor cost, suboptimal handling of goods and internal and external thefts. These downsides cause losses in both time and profitability and lead to inefficent warehouse management.
Our Solution
In this project, we are trying to address this issue by developing a fully automated warehouse management which will minimize the drawbacks while improving efficiency and profitability. We are implementing a warehouse managament system which consists two types of robots; robots arms - to handle loading/unloading of goods, automated guided vehicles(AGVs) to transport goods inside warehouse. Also an online shopping portal to make the purchases from the warehouse.
Once a customer places an order, the order will be received, processed and will be delivered to the delivery station without any human involvement. The customer will then be informed to pickup his/her order from the warehouse.
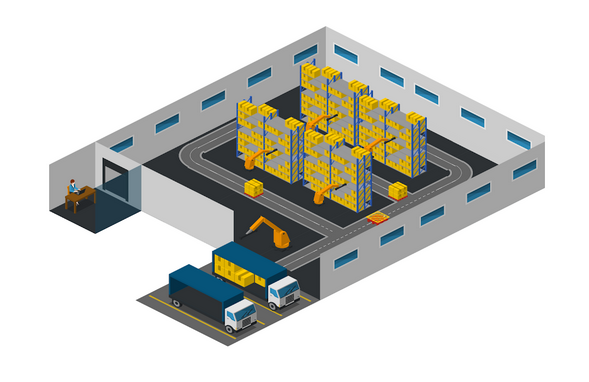
How It Works

Our solution consists three components :-
-
Fully automated warehouse
-
Controller interface to control and override(if necessary) the autonomous operations
-
Warehouse database with an online shopping portal, as an interface to retailers to make their purchases
The warehouse has two base stations, the delivery post and receiving post, to deliver goods to the customers and receive any stocks to the warehouse respectively. In these base stations, two fixed robot arms are placed to do the loading and unloading process for goods. Inside the warehouse, movable robot arms are placed among shelves to load and unload the goods to AGVs.
Once a client places an order, the database is updated and the computer fetches the relevant information about the goods and triggers up the local warehouse controller. The warehouse controller then generates instructions and are passed to the robot arm and the delivery robot to perform the task. Here, the local controller sends status messages like Insert, Takeout, Store etc. while they are processing the goods. Once the fetching of goods is done, they are delivered to the client.
When more than one orders are received, a queueing algorithm will process them and will assign the automated guided robots (AGVs) nearby those relevant shelves in such a way that no collision will occur as well as no AGV will have an overloaded queue. This queueing algorithm will assure that all AGVs and robot arms are used efficiently. A separate algorithm will choose the shortest path for AGVs to reach their destination, minimizing the travel time.

Hardware & Software Designs
The current progress and the implementations of the project can be viewed from the following links:
Demonstrations and Testing
1.Website
2.RobotArm
3.AGV V2
5.Scheduling and Path Planning
6.Integrated Simulation Enviroment
Bill of Material

Final Demonstration
1.Software
2.ARM
3.agv