RV32IM Pipelined Processor Design
Team
- E/20/032, Bandara A.M.N.C., e20032@eng.pdn.ac.lk
- E/20/034, Bandara G.M.M.R., e20034@eng.pdn.ac.lk
- E/20/157, Janakantha S.M.B.G., e20157@eng.pdn.ac.lk
Table of Contents
- Abstract
- Datapath
- Supported Instructions
- Features
- Hazard Handling
- How to Build & Simulate
- References
- Links
Abstract
This project focuses on the design and implementation of a custom 32-bit RISC-V processor supporting the RV32IM instruction set architecture (ISA). Developed as part of the Advanced Computer Architecture course (CO502), the processor encompasses essential features of the RISC-V standard, including integer operations (RV32I) and multiplication/division (M extension).
Datapath
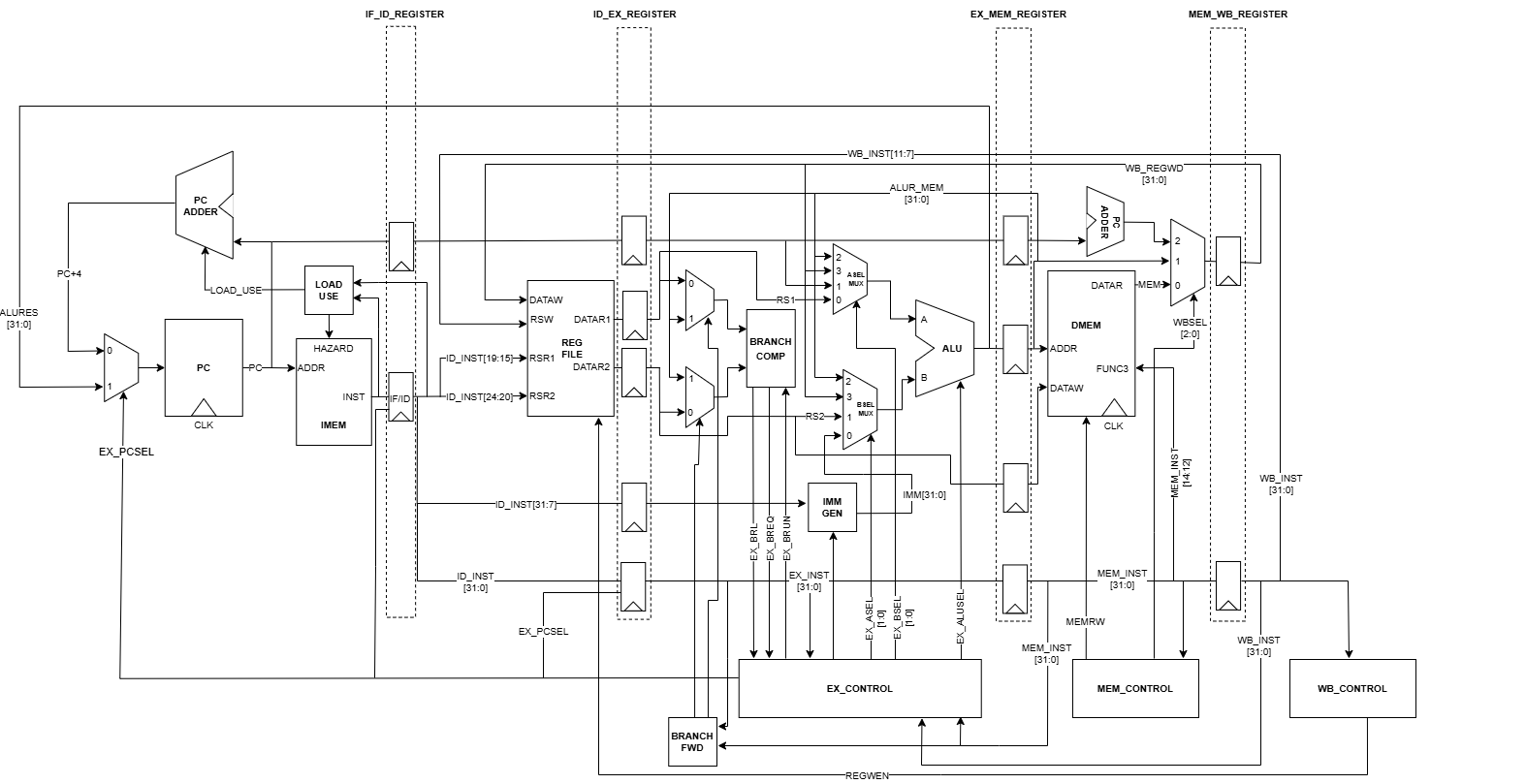
Supported Instructions
| Opcode | Instruction | Format | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0110011 | ADD | R-Type | rD = rS1 + rS2 | add r3, r1, r2 |
| 0110011 | SUB | R-Type | rD = rS1 - rS2 | sub r3, r1, r2 |
| 0110011 | AND | R-Type | rD = rS1 & rS2 | and r3, r1, r2 |
| 0110011 | OR | R-Type | rD = rS1 | rS2 | or r3, r1, r2 |
| 0110011 | XOR | R-Type | rD = rS1 ^ rS2 | xor r3, r1, r2 |
| 0110011 | SLL | R-Type | rD = rS1 « rS2 | sll r3, r1, r2 |
| 0110011 | SLT | R-Type | rD = if (rS1 < rS2) return True | slt r3, r1, r2 |
| 0110011 | SLTU | R-Type | rD = if (rS1(uint) < rS2(uint)) return True | sltu r3, r1, r2 |
| 0110011 | SRA | R-Type | rD = rS1 »> rS2 | sra r3, r1, r2 |
| 0110011 | MUL | R-Type (M) | rD = (rS1 * rS2) [31:0] | mul r3, r1, r2 |
| 0110011 | MULU | R-Type (M) | rD = (rS1(uint) * rS2(uint)) [31:0] | mulu r3, r1, r2 |
| 0110011 | MULH | R-Type (M) | rD = (rS1 * rS2) [63:32] | mulh r3, r1, r2 |
| 0110011 | MULHU | R-Type (M) | rD = (rS1(uint) * rS2(uint)) [63:32] | mulhu r3, r1, r2 |
| 0110011 | DIVU | R-Type (M) | rD = (rS1(uint) / rS2(uint)) | divu r3, r1, r2 |
| 0110011 | DIV | R-Type (M) | rD = rS1 / rS2 | div r3, r1, r2 |
| 0110011 | REM | R-Type (M) | rD = rS1 % rS2 | rem r3, r1, r2 |
| 0010011 | ADDI | I-Type | rD = rS1 + imm | addi r3, r1, 10 |
| 0010011 | SLTI | I-Type | rD = if (rS1 < imm) return True | slti r3, r1, 0xFF |
| 0010011 | SLTIU | I-Type | rD = if (rS1(uint) < rS2(uint)) return True | sltiu r3, r1, 0xFF |
| 0010011 | SLLI | I-Type | rD = rS1 « imm | slli r3, r1, 0xFF |
| 0010011 | SRAI | I-Type | rD = rS1 »> imm | srai r3, r1, 0xFF |
| 0010011 | ORI | I-Type | rD = rS1 | imm | ori r3, r1, 0xFF |
| 0010011 | XORI | I-Type | rD = rS1 ^ imm | xori r3, r1, 0xFF |
| 0000011 | LB | I-Type | Load byte from memory | lb r3, 0(r1) |
| 0000011 | LBU | I-Type | Load byte unsigned from memory | lbu r3, 0(r1) |
| 0000011 | LH | I-Type | Load halfword from memory | lh r3, 0(r1) |
| 0000011 | LHU | I-Type | Load halfword unsigned from memory | lhu r3, 0(r1) |
| 0000011 | LW | I-Type | Load word from memory | lw r3, 0(r1) |
| 0100011 | SB | S-Type | Store byte to memory | sb r3, 0(r1) |
| 0100011 | SH | S-Type | Store halfword to memory | sh r3, 0(r1) |
| 0100011 | SW | S-Type | Store word to memory | sw r3, 0(r1) |
| 1100011 | BEQ | B-Type | Branch if equal | beq r1, r2, label |
| 1100011 | BNE | B-Type | Branch if not equal | bne r1, r2, label |
| 1100011 | BLT | B-Type | Branch if less than | blt r1, r2, label |
| 1100011 | BGE | B-Type | Branch if greater than or equal | bge r1, r2, label |
| 1100011 | BLTU | B-Type | Branch if less than (uint) | bltu r1, r2, label |
| 1100011 | BGEU | B-Type | Branch if greater than or equal (uint) | bgeu r1, r2, label |
| 1101111 | JAL | J-Type | Jump and link | jal r1, label |
| 1100111 | JALR | I-Type | Jump and link register | jalr r1, r2, 0 |
| 0110111 | LUI | U-Type | Load upper immediate | lui r1, 0x12345 |
| 0010111 | AUIPC | U-Type | Add upper immediate to PC | auipc r1, 0x1000 |
Features
- 5-Stage Pipeline: IF, ID, EX, MEM, WB
- Hazard Handling:
- Load-use hazard detection and NOP insertion
- Control hazard handling with pipeline flushing
- Data hazard mitigation via forwarding
- Memory Unit: Supports load/store operations (LB, LH, LW, SB, SH, SW)
- ALU Operations: Supports arithmetic, logical, and branching instructions
- Register File: 32 general-purpose registers with asynchronous reads
- Instruction Memory (IMEM) & Data Memory (DMEM)
Hazard Handling
The processor handles hazards using the following techniques:
Load-Use Hazard: Detects dependencies between load instructions and subsequent dependent instructions. Inserts a NOP to the pipeline.
Data Hazard: Uses a Forwarding Unit to forward register values from MEM and WB stages to EX stage.
Control Hazard: Implements pipeline flushing and instruction replacement when a branch is taken.
How to Build and Simulate
Requirements
- VHDL Simulator (ModelSim, GHDL, Xilinx Vivado)
- GTKWave
Simulate
Navigate to the working directory and make sure all files are in the directory. Analyze all .vhdl files before running main.vhdl:
./analyze.sh
References
- Hennessy, J. L., & Patterson, D. A. (2020). Computer Architecture: A Quantitative Approach.
- IEEE Std 1800-2019: SystemVerilog—Unified Hardware Design.
- Installing GHDL and GTKWave: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0JJku1vTu78
- Learn VHDL: https://nandland.com/learn-vhdl/
