Handling Data Hazards
Most data hazards can be resolved by using a forwarding mechanism. Load-use data hazard cannot be completely resolved using a forwarding mechanism but the hazard can be minimised upto a certain extent. In a pipeline processor with forwarding, there are 4 forwarding paths.
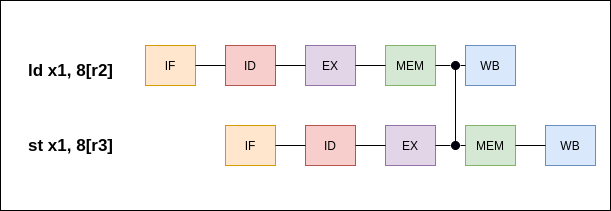
RW/MEM Forwarding Path
ld x1, 8[x2] st x1, 8[x3] The data loaded from memory is needed to perform the store operation before the load instruction writes back to the register R1.
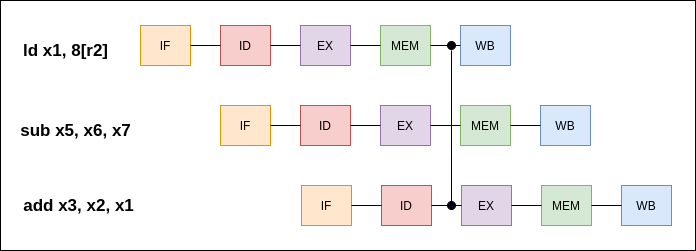
RW/EXE Forwarding Path
ld x1, 8[x2] sub x5, x6, x7 add x3, x2, x1 The data loaded from memory is needed to perform the add operation before the load instruction writes back to the register R1.
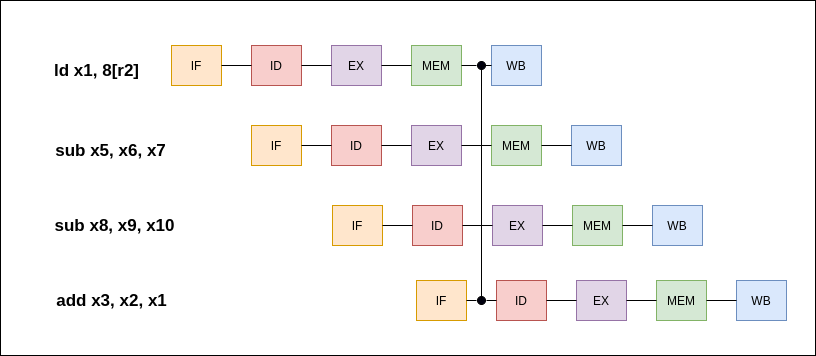
RW/ID Forwarding Path
ld x1, 8[x2] sub x5, x6, x7 sub x8, x9, x10 add x3, x2, x1 The data loaded from memory is needed to perform the add operation before the load instruction writes back to the register R1.
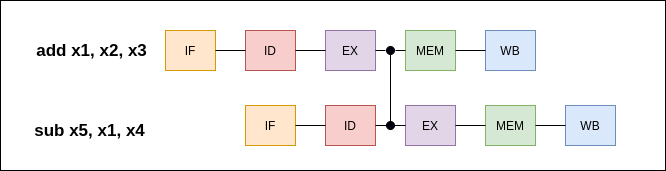
MEM/EXE Forwarding Path
add x1, x2, x3 sub x5, x1, x4 The alu result from the add instruction is needed to the sub instruction before it writes to the register R1.
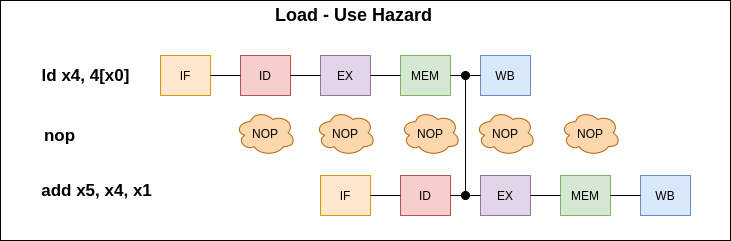
Handling Load-Use Hazard with Forwarding and Nop
ld x4, 4[x0] add x5, x4, x1 The data loaded from memory is needed to perform the add operation before the load instruction writes back to the register R4.
In Load-Use hazards,it is required to have a nop because the data isready in the mem stage at the end of the clock cycle and instruction after the Load instruction needs the loaded data at the beginning of the clock cycle.